Research
Mechanical Analysis of Cardiomyocyte Contraction
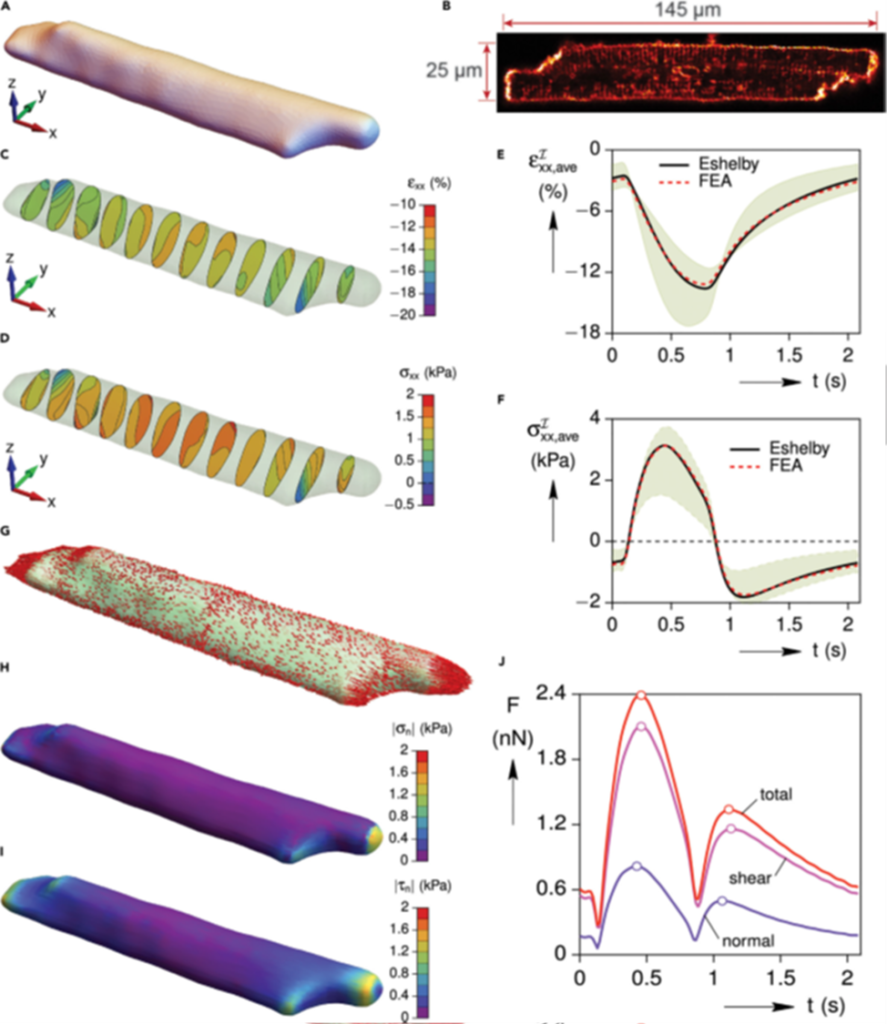
The heart pumps blood into circulation against the mechanical load from the vascular resistance. Mechanical overload such as high blood pressure leads to heart diseases. To study the mechano-transduction mechanisms, we invented an innovative Cell-in-Gel technology to control the mechanical load on single cardiomyocytes during cell contraction in a 3-D viscoelastic hydrogel mimicking the in-situ environment. We combine experiments and modeling to quantify the 3-D mechanical strain and stress in cardiomyocytes, showing longitudinal tension, transverse compression, and surface traction (normal and shear stress) in the cell during beat-to-beat contraction.
Publication List (in reverse chronological order)
| 4. | Kazemi-Lari MA, Shimkunas R, Jian Z, Hegyi B, Izu L, Shaw JA, Wineman AS, Chen-Izu Y. Modeling cardiomyocyte mechanics and autoregulation of contractility by mechano-chemo-transduction feedback. iScience. 2022 Jun 26;25(7):104667. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104667. eCollection 2022 Jul 15. PMID: 35860762. |
| 3. | Mohammad Ali Kazemi-Lari; John Shaw*, Alan S. Wineman; Rafael Shimkunas; Zhong Jian; Bence Hegyi; Leighton Izu; Chen-Izu Y. Viscoelastic Eshelby Inclusion Model and Analysis of the Cell-in-Gel System. International Journal of Engineering Science. Vol.165, 1 Aug 2021,103489. (2014). |
| 2. | Shaw, J, Izu, L, Chen-Izu, Y. Mechanical analysis of single myocyte contraction in a 3-d elastic matrix. PloS one, 8(10): e75492 (2013). |
| 1. | Awasthi S, Izu LT, Mao Z, Jian Z, Landas T, Lerner A, Shimkunas R, Woldeyesus R, Bossuyt J, Wood B, Chen YJ, Matthews DL, Lieu DK, Chiamvimonvat N, Lam KS, Chen-Izu Y*, Chan JW*. Multimodal SHG-2PF Imaging of Microdomain Ca2+-Contraction Coupling in Live Cardiac Myocytes. Circulation Research 22:118(2):e19-28 (2016). |