Research
Mechano-Electro-Transduction
The heart is an electro-mechanical pump. The heart rhythm is coordinated by electrical action potentials that trigger Ca2+ signaling and cardiomyocyte contraction. The mechanical load during contraction can also feedback to affect the electrophysiology. Mechanical overload may lead to disruption of the action potential leading to arrhythmias. However, the mechanisms underlying mechano-electric coupling in cardiomyocytes remain unclear.
We developed the Patch-Clamp-in-Gel technology to investigate how the mechanical load on the cell affects the action potential and ion channels in the cardiomyocyte. Our data show that mechanical load prolonged action potential duration (APD), increased transient outward K+ current, decreased inward rectifier K+ current, and increased L-type Ca2+ current. Increased Ca2+ entry caused elevated SR Ca2+ load, increased cytosolic Ca2+ transient (CaT) and enhanced contractility. However, mechanical overload caused discordant alternans in APD and CaT which may lead to arrhythmias.
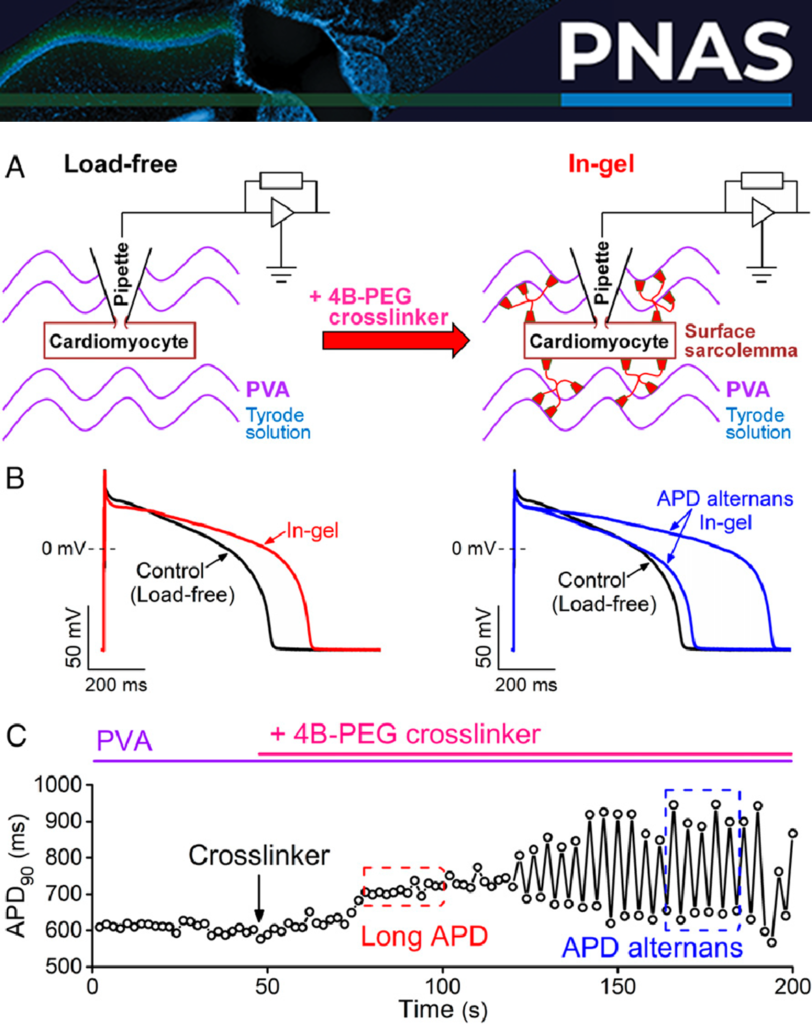
| 2. | Hegyi B, Shimkunas R, Jian Z, Izu LT, Bers DM, Chen-Izu Y*. Mechanoelectric coupling and arrhythmogenesis in cardiomyocytes contracting under mechanical afterload in a 3D viscoelastic hydrogel. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences USA (PNAS). 2021;118(31):e2108484118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108484118. |
| 1. | Shimkunas R, Hegyi B, Jian Z, Shaw JA, Kazemi-Lari MA, Mitra D, Leach JK, Li X, Jaradeh M, Balardi N, Chen YJ, Escobar AL, Baker AJ, Bossuyt J, Banyasz T, Chiamvimonvat N, Lam KS, Bers DM, Izu LT, Ye Chen-Izu. Mechanical Load Regulates Excitation-Ca 2+ Signaling-Contraction in Cardiomyocyte. Circulation Research. 2021 Mar 19;128(6):772-774. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318570. Epub 2021 Feb 19. |